Variant Calling Workflow
Nextflow Variant Calling
First, let’s create a new directory called workflow and navigate to it:
mkdir workflow
cd workflow
Variant Calling Workflow
Our variant calling workflow has the following steps:
- Index the reference genome for use by
bwa. - Align reads to the reference genome using
bwa mem. - Convert the aligned SAM file to BAM format using
samtools. - Convert the format of the alignment to sorted BAM, with some intermediate steps.
- Calculate the read coverage of positions in the genome.
- Detect the single nucleotide variants (SNVs).
- Filter and report the SNVs in VCF (variant calling format).
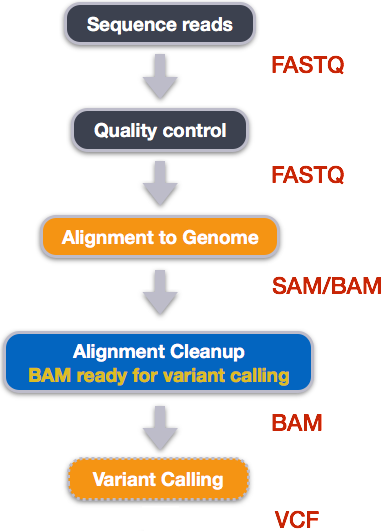
- Read more about the variant-calling pipeline here -> Data Carpentry: Wrangling Genomics Lesson
Variant-Calling BASH script
set -e
mkdir /workspace/nextflow_tutorial/bash-results
cd /workspace/nextflow_tutorial/bash-results
genome=/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/ref_genome/ecoli_rel606.fasta
bwa index $genome
mkdir -p sam bam bcf vcf
for fq1 in /workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/trimmed_fastq/*_1.trim.fastq.gz;
do
echo "working with file $fq1"; base=$(basename $fq1 _1.trim.fastq.gz); echo "base name is $base" \
fq1=/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/trimmed_fastq/${base}_1.trim.fastq.gz
fq2=/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/trimmed_fastq/${base}_2.trim.fastq.gz
sam=/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/results/sam/${base}.aligned.sam
bam=/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/results/bam/${base}.aligned.bam
sorted_bam=/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/results/bam/${base}.aligned.sorted.bam
raw_bcf=/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/results/bcf/${base}_raw.bcf
variants=/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/results/vcf/${base}_variants.vcf
final_variants=/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/results/vcf/${base}_final_variants.vcf
bwa mem $genome $fq1 $fq2 > $sam
samtools view -S -b $sam > $bam
samtools sort -o $sorted_bam $bam
samtools index $sorted_bam
bcftools mpileup -O b -o $raw_bcf -f $genome $sorted_bam
bcftools call --ploidy 1 -m -v -o $variants $raw_bcf
vcfutils.pl varFilter $variants > $final_variants
done
Variant Calling Nextflow Pipeline
Now, let’s create a new Nextflow script named variant-calling.nf:
code variant-calling.nf
You can now start implementing your Nextflow pipeline by following the provided workflow steps. Be sure to define the input channels for each process and utilize the Nextflow syntax when writing your pipeline. You can refer to the Nextflow documentation for syntax, process definition, and examples.
In the variant-calling.nf script, you will be converting the BASH commands from the provided script into Nextflow processes. You can use the input and output directives to define input and output files for each process. You can also use Nextflow operators like view, split, and join to manipulate channels. Additionally, you can use thescriptdirective to embed the BASH commands directly into the Nextflow processes. Remember to make use of theparams` feature to make your pipeline more flexible and configurable.
/*
========================================================================================
Variant-Calling Nextflow Workflow
========================================================================================
Github :
Contact :
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
nextflow.enable.dsl=2
// Pipeline Input parameters
params.outdir = 'results'
params.genome = "/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/ref_genome/ecoli_rel606.fasta"
params.reads = "/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/trimmed_fastq/*_{1,2}.trim.fastq.gz"
println """\
V A R I A N T-C A L L I N G - N F P I P E L I N E
===================================
genome : ${params.genome}
reads : ${params.reads}
outdir : ${params.outdir}
"""
.stripIndent()
/*
========================================================================================
Create Channels
========================================================================================
*/
ref_ch = Channel.fromPath( params.genome, checkIfExists: true )
reads_ch = Channel.fromFilePairs( params.reads, checkIfExists: true )
/*
========================================================================================
MAIN Workflow
========================================================================================
*/
workflow {
FASTQC( reads_ch )
BWA_INDEX( ref_ch )
BWA_ALIGN( BWA_INDEX.out.bwa_index.combine(reads_ch) ) // https://www.nextflow.io/docs/latest/process.html#understand-how-multiple-input-channels-work
SAMTOOLS_SORT( BWA_ALIGN.out.aligned_bam )
// Enter the rest of the processes for variant calling based on the bash script below
}
/*
========================================================================================
Processes
========================================================================================
*/
/*
* Align reads to reference genome & create BAM file.
*/
process FASTQC {
tag{"FASTQC ${reads}"}
label 'process_low'
publishDir("${params.outdir}/fastqc_trim", mode: 'copy')
input:
tuple val( sample_id ), path( reads )
output:
path( "*_fastqc*" ), emit: fastqc_out
script:
"""
fastqc ${reads}
"""
}
/*
* Index the reference genome for use by bwa and samtools.
*/
process BWA_INDEX {
tag{"BWA_INDEX ${genome}"}
label 'process_low'
publishDir("${params.outdir}/bwa_index", mode: 'copy')
input:
path genome
output:
tuple path( genome ), path( "*" ), emit: bwa_index
script:
"""
bwa index ${genome}
"""
}
/*
* Align reads to reference genome & create BAM file.
*/
process BWA_ALIGN {
tag{"BWA_ALIGN ${sample_id}"}
label 'process_medium'
publishDir("${params.outdir}/bwa_align", mode: 'copy')
input:
tuple path( genome ), path( "*" ), val( sample_id ), path( reads )
output:
tuple val( sample_id ), path( "${sample_id}.aligned.bam" ), emit: aligned_bam
script:
"""
INDEX=`find -L ./ -name "*.amb" | sed 's/.amb//'`
bwa mem \$INDEX ${reads} > ${sample_id}.aligned.sam
samtools view -S -b ${sample_id}.aligned.sam > ${sample_id}.aligned.bam
"""
}
/*
* Convert the format of the alignment to sorted BAM.
*/
process SAMTOOLS_SORT {
tag{"SAMTOOLS_SORT ${sample_id}"}
label 'process_low'
publishDir("${params.outdir}/bam_align", mode: 'copy')
input:
tuple val( sample_id ), path( bam )
output:
tuple val( sample_id ), path( "${sample_id}.aligned.sorted.bam" ), emit: sorted_bam
script:
"""
samtools sort -o "${sample_id}.aligned.sorted.bam" ${bam}
"""
}
/*
* Index the BAM file for visualization purpose
*/
process SAMTOOLS_INDEX {
}
/*
* Calculate the read coverage of positions in the genome.
*/
process BCFTOOLS_MPILEUP {
}
/*
* Detect the single nucleotide variants (SNVs).
*/
process BCFTOOLS_CALL {
}
/*
* Filter and report the SNVs in VCF (variant calling format).
*/
process VCFUTILS {
}
/*
========================================================================================
Workflow Event Handler
========================================================================================
*/
workflow.onComplete {
println ( workflow.success ? """
Pipeline execution summary
---------------------------
Completed at: ${workflow.complete}
Duration : ${workflow.duration}
Success : ${workflow.success}
workDir : ${workflow.workDir}
exit status : ${workflow.exitStatus}
""" : """
Failed: ${workflow.errorReport}
exit status : ${workflow.exitStatus}
"""
)
}
/*
========================================================================================
THE END
========================================================================================
*/
For each process, define the required input and output files using the input and output directives. Make sure to declare the necessary executables, such as bwa, samtools, bcftools, and vcfutils.pl, within the script directive as needed.
Throughout the development of your pipeline, consult the Nextflow documentation for specific syntax, operators, and other features that may help in creating an efficient and well-structured pipeline. Once you have completed the variant-calling.nf script, you can execute it using the nextflow run command, providing any necessary parameters and configurations as needed.
In this section, we will discuss how to run a Nextflow workflow and handle completion events, as well as generate metrics and reports. To run the variant-calling.nf script, use the following command:
nextflow run variant-calling.nf
To understand how multiple input channels work in Nextflow, you can refer to the documentation.
Handle completion event
Handling the completion event is essential to know when your pipeline has finished executing. Nextflow provides the workflow.onComplete event handler for this purpose. You can add this code block to your variant-calling.nf script to print a confirmation message when the script completes:
workflow.onComplete {
println ( workflow.success ? """
Pipeline execution summary
---------------------------
Completed at: ${workflow.complete}
Duration : ${workflow.duration}
Success : ${workflow.success}
workDir : ${workflow.workDir}
exit status : ${workflow.exitStatus}
""" : """
Failed: ${workflow.errorReport}
exit status : ${workflow.exitStatus}
"""
)
}
This code utilizes the ternary operator, which is a concise way of writing an if/else branch:
expression_is_true ? "set_value_to_a" : "set_value_to_b"
Metrics and reports
Nextflow is capable of generating various reports and charts, providing runtime metrics and execution information. You can enable these options when running your script:
-with-report: Creates a workflow execution report.-with-trace: Generates a tab-separated file containing runtime information for each executed task, such as submission time, start time, completion time, CPU, and memory usage.-with-timeline: Produces a workflow timeline report, which helps identify time-consuming tasks and bottlenecks.-with-dag: Renders a directed acyclic graph representation of the workflow execution. This feature requires the installation of Graphviz, an open-source graph visualization software.
To run the workflow with these options, use the following command:
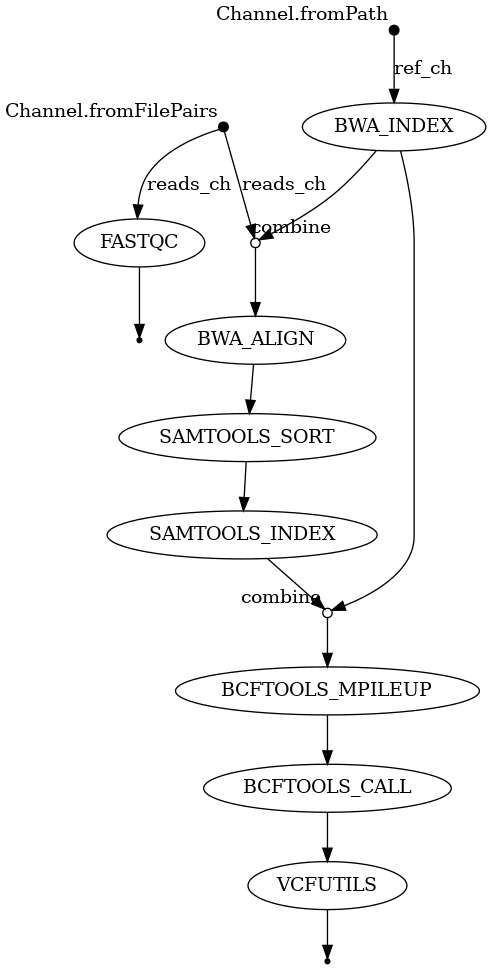
nextflow run variant-calling.nf -resume -with-report -with-trace -with-timeline -with-dag dag.png
Your final Nextflow workflow DAG image should resemble this:
Quick Recap:
- Nextflow can combine tasks (processes) and manage data flows using channels within a single pipeline/workflow.
- A workflow can be parameterized using
params. The values of these parameters can be captured in a log file usinglog.info. - Workflow steps are connected via their inputs and outputs using Channels.
- Nextflow can execute an action when the pipeline completes the execution using the
workflow.onCompleteevent handler to print a confirmation message. - Nextflow can produce multiple reports and charts, providing runtime metrics and execution information using the command-line options
-with-report,-with-trace,-with-timeline, and-with-dag.