Nextflow Channels
Nextflow Channels
mkdir channels
cd channels
- Channels are how Nextflow handles file management, allowing complex tasks to be split up, run in parallel, and reduces ‘admin’ required to get the right inputs to the right parts of the pipeline.
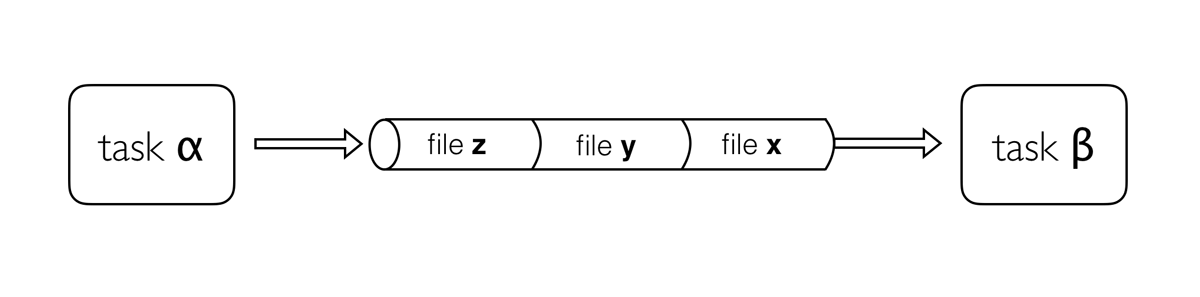
- Channels connect processes via their
inputsandoutputs. - Channels can store multiple items, such as files (e.g., fastq files) or values.
- The number of items a channel stores determines how many times a process will run using that channel as input. When the process runs using one item from the input channel, we will call that run a task.
- Channels are asynchronous, which means that output data from a set of processes will not necessarily be output in the same order as they went in.
- However, the first element into a queue is the first out of the queue (First in-First out). This allows processes to run as soon as they receive input from a channel. Channels only send data in one direction, from a producer (a process/operator), to a consumer (another process/operator).
- Nextflow distinguishes between two different kinds of channels:
valuechannelsqueuechannels
Value channels
- A value channel is bound to a single value.
- A value channel can be used an unlimited number of times since its content is not consumed. This is also useful for processes that need to reuse input from a channel, for example, a reference genome sequence file that is required by multiple steps within a process, or by more than one process.
- The
valuefactory method is used to create a value channel. Values are put inside parentheses()to assign them to a channel.
Create a Nextflow file called value_ch.nf; add the following and execute it using nextflow run value_ch.nf:
// Creates an empty value channel.
ch1 = Channel.value('GRCh38')
// Creates a value channel and binds a string to it.
ch2 = Channel.value(['chr1', 'chr2', 'chr3', 'chr4', 'chr5'])
// Creates a value channel and binds a list object to it that will be emitted as a single item.
ch3 = Channel.value(['chr1': 248956422, 'chr2': 242193529, 'chr3': 198295559])
// The value method can only take 1 argument, however, this can be a single list containing several elements.
ch1.view()
ch2.view()
ch3.view()
Output
N E X T F L O W ~ version 21.04.3 Launching `value_ch.nf` [happy_bell] - revision: a80c27d5b2 GRCh38 [chr1, chr2, chr3, chr4, chr5] [chr1:248956422, chr2:242193529, chr3:198295559]
Reminder:
- A List object can be defined by placing the values in square brackets [] separated by a comma.
- A Map object is similar, but with
key:value pairsseparated by commas.Example:
myList = [1776, -1, 33, 99, 0, 928734928763] myMap = [ p1 : "start", q2 : "end" ]
Queue channel
Queuechannels are a type of channel in which data is consumed (used up) to provide input for a process/operator.- Queue channels can be created in two ways:
- As the outputs of a process.
- A queue channel can be explicitly created using channel factory methods such as Channel.of or Channel.fromPath.
In Nextflow DSL1, queue channels can only be used once in a workflow, either connecting workflow input to process input, or process output to input for another process. In DSL2, we can use a queue channel multiple times.
What is the difference between a queue and value channel?
- A queue channel is consumable and can store multiple values.
- A value channel, also known as a singleton channel, is bound to a single value by definition.
Queue channel factory
-
Channel factories are used to explicitly create channels. Channel factories are called using the
Channel.<method>syntax and return a specific instance of a Channel. -
Queue(consumable) channels can be created using the following channel factory methods:
Create a Nextflow file called queue_channel.nf; add the following and execute it using nextflow run queue_channel.nf:
// Create a queue channel using the Channel.of factory method
ch1 = Channel.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
// Create a queue channel using the Channel.fromList factory method
ch2 = Channel.fromList(['A', 'B', 'C'])
// Create a queue channel using the Channel.fromPath factory method (adjust the path to an existing file in your system)
ch3 = Channel.fromPath('/path/to/your/file.txt')
ch1.view()
ch2.view()
ch3.view()
Output
N E X T F L O W ~ version 21.04.3 Launching `queue_channel.nf` [serene_babbage] - revision: 12345678 1 2 3 4 5 A B C /path/to/your/file.txt
1. The of Channel factory
- When you want to create a channel containing multiple values, you can use the channel factory
Channel.of. Channel.ofallows the creation of aqueuechannel with the values specified as arguments, separated by a comma,.- You can specify a range of numbers as a single argument using the Groovy range operator
... This creates each value in the range (including the start and end values) as a value in the channel. The Groovy range operator can also produce ranges of dates, letters, or time. More information on the range operator can be found here.
Create a Nextflow file called queue_of.nf; add the following to create a Channel.of method and execute it using nextflow run queue_of.nf:
chromosome_ch = Channel.of('chr1', 'chr3', 'chr5', 'chr7')
chromosome_ch2 = Channel.of(1..22, 'X', 'Y')
chromosome_ch.view()
chromosome_ch2.view()
Output
N E X T F L O W ~ version 21.04.3 Launching `queue_of.nf` [modest_miescher] - revision: fb9862a33f chr1 chr3 chr5 chr7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 X Y
- The first line in this example creates a variable
chromosome_ch.chromosome_chis a queue channel containing the four values specified as arguments in theofmethod. The.viewoperator will print one line per item in a list. Therefore the view operator on the second line will print four lines, one for each element in the channel.- Arguments passed to the
ofmethod can be of varying types e.g., combinations of numbers, strings, or objects. In the above examples, we have examples of both string and number data types.
2. The fromList Channel factory
- You can use the
Channel.fromListmethod to create a queue channel from a list object.
Create a new file queue_list.nf; add the following and execute it using nextflow run queue_list.nf:
aligner_list = ['salmon', 'kallisto']
aligner_ch = Channel.fromList(aligner_list)
aligner_ch.view()
Output
N E X T F L O W ~ version 21.04.3 Launching `queue_list.nf` [admiring_raman] - revision: b2dec22cea salmon kallistoIn this example, we first create a list object called
aligner_listcontaining two strings, ‘salmon’ and ‘kallisto’. We then use theChannel.fromListmethod to create a queue channel namedaligner_chfrom thealigner_list. Finally, we use the.view()operator to display the content of the channel.
Channel.fromListvsChannel.ofIn the above example, the channel has two elements. If you had used theChannel.of(list)it would have contained only 1 element [salmon, kallisto] and any operator or process using the channel would run once.
CLICK HERE for an exercise on creating channels from a list
Create a Nextflow script `exercise_1.nf` that creates both a `queue` and `value` channel for the following list. Then print the contents of the channels using the view operator. How many lines does the queue and value channel print? ```groovy ids = ['ERR908507', 'ERR908506', 'ERR908505'] ``` Solution ```groovy ids = ['ERR908507', 'ERR908506', 'ERR908505'] queue_ch = Channel.fromList(ids) value_ch = Channel.value(ids) queue_ch.view() value_ch.view() ``` Output ``` N E X T F L O W ~ version 21.04.3 Launching `exercise_1.nf` [silly_hypatia] - revision: 5d8381b7d4 ERR908507 ERR908506 ERR908505 [ERR908507, ERR908506, ERR908505] ``` ``` The queue channel `queue_ch` will print three lines. The value channel `value_ch` will print one line. ``` ##3. The fromPath Channel factory
-
The previous channel factory methods dealt with sending general values in a channel. A special channel factory method
fromPathis used when wanting to pass files. - The
fromPathfactory method creates a queue channel emitting one or more files matching a file path. - The file path (written as a quoted string) can be the location of a single file or a “glob pattern” that matches multiple files or directories.
A glob pattern is specified as a string and is matched against directory or file names.
- An asterisk,
*, matches any number of characters (including none). - Two asterisks,
**, works like*but will also search sub directories. This syntax is generally used for matching complete paths. - Braces
{}specify a collection of subpatterns. For example:{bam,bai}matchesbamorbai
- An asterisk,
-
The file path can be a relative path (path to the file from the current directory), or an absolute path (path to the file from the system root directory - starts with
/). - You can change the behaviour of
Channel.fromPathmethod by changing its options. A list of.fromPathoptions is shown below: - In Nextflow, method parameters are separated by a
,and parameter values specified with a colon:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| glob | When true, the characters *, ?, [] and {} are interpreted as glob wildcards, otherwise they are treated as literal characters (default: true) |
| type | The type of file paths matched by the string, either file, dir or any (default: file) |
| hidden | When true, hidden files are included in the resulting paths (default: false) |
| maxDepth | Maximum number of directory levels to visit (default: no limit) |
| followLinks | When true, symbolic links are followed during directory tree traversal, otherwise they are managed as files (default: true) |
| relative | When true returned paths are relative to the top-most common directory (default: false) |
| checkIfExists | When true throws an exception if the specified path does not exist in the file system (default: false) |
Create a new file queue_path.nf; add the following and nextflow run queue_path.nf:
println("Single File")
read_ch = Channel.fromPath("/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/SRR2584863_1.fastq.gz")
read_ch.view()
println("Glob Syntax")
// We can change the default options for the `fromPath` method to give an error if the file doesn’t exist using the `checkIfExists` parameter.
read_ch = Channel.fromPath( "/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/*.fastq.gz", checkIfExists: true )
read_ch.view()
// **Note The pattern must contain at least a star wildcard character.**
Output
N E X T F L O W ~ version 21.04.3 Launching `queue_path.nf` [awesome_yalow] - revision: 695fc25ebf Single File /workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/SRR2584863_1.fastq.gz Glob Syntax /workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/SRR2589044_
4. The fromFilePairs Channel factory
- We have seen how to process files individually using
fromPath. In Bioinformatics we often want to process files in pairs or larger groups, such as read pairs in sequencing.
For example in the /workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq directory we have three groups of read pairs:
| Sample_ID | read1 | read2 |
|---|---|---|
| SRR2589044 | SRR2589044_1.fastq.gz | SRR2589044_2.fastq.gz |
| SRR2584863 | SRR2584863_1.fastq.gz | SRR2584863_2.fastq.gz |
| SRR2584866 | SRR2584866_1.fastq.gz | SRR2584866_2.fastq.gz |
-
Nextflow provides a convenient factory method for this common bioinformatics use case. The
fromFilePairsmethod creates a queue channel containing a tuple for every set of files matching a specific pattern (e.g.,/path/to/*_{1,2}.fastq.gz). -
A tuple is a grouping of data, represented as a Groovy List.
- The first element of the tuple emitted from
fromFilePairsis a string based on the shared part of the filenames (i.e., the*part of the glob pattern). - The second element is the list of files matching the remaining part of the glob pattern (i.e., the
<string>_{1,2}.fastq.gz pattern). This will include any files ending_1.fastq.gzor_2.fastq.gz.
- The first element of the tuple emitted from
Create a new queue_pairs.nf; add the following and nextflow run queue_pairs.nf:
read_pair_ch = Channel.fromFilePairs("/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/*_{1,2}.fastq.gz", checkIfExists: true)
read_pair_ch.view()
Output
N E X T F L O W ~ version 21.04.3 Launching `queue_pairs.nf` [nauseous_austin] - revision: eb531c1c8a [SRR2589044, [nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/SRR2589044_1.fastq.gz, nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/SRR2589044_2.fastq.gz]] [SRR2584863, [nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/SRR2584863_1.fastq.gz, nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/SRR2584863_2.fastq.gz]] [SRR2584866, [nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/SRR2584866_1.fastq.gz, nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/SRR2584866_2.fastq.gz]]This will produce a queue channel,
read_pair_ch, containing three elements:
-
Each element is a tuple that has:
- string value (the file prefix matched, e.g
SRR2584866) - and a list with the two files e,g. [
/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/SRR2584866_1.fastq.gz, /workspace/nextflow_tutorial/data/untrimmed_fastq/SRR2584866_2.fastq.gz] .
- string value (the file prefix matched, e.g
- The asterisk character
*, matches any number of characters (including none), and the{}braces specify a collection of subpatterns. - Therefore the
*_{1,2}.fastq.gzpattern matches any file name ending in_1.fastq.gzor_2.fastq.gz.
Read more information about the channel factory
fromFilePairshere
5. The fromSRA Channel factory
-
The
fromSRAmethod makes it possible to query the NCBI SRA archive and returns a queue channel emitting the FASTQ files matching the specified selection criteria. -
Read more about
fromSRAChannel factory here
Quick Recap:
- Channels must be used to import data into Nextflow.
- Nextflow has two different kinds of channels,
queuechannels andvaluechannels.- Data in
valuechannels can be used multiple times in a workflow.- Data in
queuechannels are consumed when they are used by a process or an operator.- Channel factory methods, such as
Channel.of, are used to create Channels.- Channel factory methods have optional parameters e.g.,
checkIfExists, that can be used to alter the creation and behavior of a channel.
Complex Multi-map Input for Channels
Quick Recap:
- Channels must be used to import data into Nextflow.
- Nextflow has two different kinds of channels,
queuechannels andvaluechannels.- Data in
valuechannels can be used multiple times in workflow.- Data in
queuechannels are consumed when they are used by a process or an operator.- Channel factory methods, such as
Channel.of, are used to create Channels.- Channel factory methods have optional parameters e.g.,
checkIfExists, that can be used to alter the creation and behaviour of a channel.