NextFlow Sub-Workflows
Nextflow Sub-Workflows
Sub-workflows in Nextflow
Sub-workflows are a chain of multiple modules providing a higher-level of functionality within a pipeline context. For instance, you could have a sub-workflow running multiple QC tools with FastQ files as input. These sub-workflows should ideally be bundled with the pipeline implementation and shared among different pipelines as needed.
Nextflow DSL2 not only allows for the definition of reusable processes (modules), but also enables the creation of reusable sub-workflow libraries.
Workflow Definition
The workflow keyword enables the definition of workflow components that enclose one or more processes and operators.
An Implicit workflow is a workflow definition that does not declare any name and is assumed to be the main workflow. It is implicitly executed, serving as the entry point of the workflow application.
A workflow component can access any variable and parameter defined in the outer scope. It can also declare one or more input channels using the take keyword.
Warning: When using the
takekeyword, the beginning of the workflow body needs to be identified with themainkeyword. Then, the input can be specified as an argument in the workflow invocation statement.
These input channels can be passed to the workflow as parameters inside the parentheses (). Multiple parameters are separated by a comma , and must be specified in the order they appear under take:.
Note: Workflow inputs are by definition channel data structures. If a basic data type is provided instead (i.e., number, string, list, etc.), it’s implicitly converted to a channel value (i.e., non-consumable).
A workflow component can declare one or more output channels using the emit keyword.
Note: Implicit workflow definition is ignored when a script is included as a module. This allows the writing of a workflow script that can be used either as a library module or as an application script.
Like modules, workflow components can be defined within your script or imported by an include statement. After which, they can then be invoked and composed as any other workflow component or process in your script.
Let’s create a sub-workflow for read qc using fastqc and multiqc modules.
- First, we need to create a new file
multiqc.nfin the/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/modules/directory; paste the following and save.
/*
========================================================================================
MULTIQC module
========================================================================================
Website: https://multiqc.info/
========================================================================================
*/
// Parameter definitions
params.CONTAINER = "quay.io/biocontainers/multiqc:1.9--pyh9f0ad1d_0"
params.OUTPUT = "multiqc_output"
process MULTIQC {
// where to store the results and in which way
publishDir(params.OUTPUT, mode: 'copy')
// indicates to use as a container the value indicated in the parameter
container( params.CONTAINER )
// show in the log which input file is analysed
tag( "${inputfiles}" )
input:
path( inputfiles )
output:
path "multiqc_report.html", emit: multiqc_report
script:
"""
multiqc .
"""
}
- Now, let’s create a new directory for subworkflows
cd /workspace/nextflow_tutorial
mkdir subworkflows
cd subworkflows
- Create a new file
fastmultiqc.nfin/workspace/nextflow_tutorial/subworkflowsdirectory; paste the following and save.
/*
========================================================================================
READ QC Sub-Workflow
========================================================================================
*/
/*
========================================================================================
Include Modules
========================================================================================
*/
include { FASTQC } from "../modules/fastqc"
include { MULTIQC } from "../modules/multiqc"
/*
========================================================================================
Workflow READ_QC
========================================================================================
*/
workflow READ_QC {
take:
reads
main:
FASTQC(reads)
MULTIQC(FASTQC.out.collect())
emit:
fastqc = FASTQC.out.fastqc_out
multiqc = MULTIQC.out.multiqc_report
}
- Move to parent directory
cd /workspace/nextflow_tutorial
- Replace your
variant-calling.nfscript as shown below to include theQCsub-workflow
/*
========================================================================================
Variant-Calling Nextflow Workflow
========================================================================================
Github :
Contact :
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
nextflow.enable.dsl=2
println """\
V A R I A N T-C A L L I N G - N F P I P E L I N E
===================================
genome : ${params.genome}
reads : ${params.reads}
outdir : ${params.outdir}
"""
.stripIndent()
/*
========================================================================================
Include Modules
========================================================================================
*/
include { BWA_INDEX } from "./modules/bwa_index" addParams(OUTPUT: "${params.outdir}/bwa_index")
include { BWA_ALIGN } from "./modules/bwa_align" addParams(OUTPUT: "${params.outdir}/bwa_align")
include { SAMTOOLS_SORT; SAMTOOLS_INDEX } from "./modules/samtools" addParams(OUTPUT: "${params.outdir}/sorted_bam")
include { BCFTOOLS_MPILEUP; BCFTOOLS_CALL; VCFUTILS } from "./modules/bcftools" addParams(OUTPUT: "${params.outdir}/vcf")
/*
========================================================================================
Include Sub-Workflows
========================================================================================
*/
include { READ_QC } from "./subworkflows/fastmultiqc" addParams(OUTPUT: "${params.outdir}/read_qc")
/*
========================================================================================
Create Channels
========================================================================================
*/
ref_ch = Channel.fromPath( params.genome, checkIfExists: true )
reads_ch = Channel.fromFilePairs( params.reads, checkIfExists: true )
/*
========================================================================================
WORKFLOW - Variant Calling
========================================================================================
*/
workflow QC {
READ_QC( reads_ch )
}
workflow {
READ_QC( reads_ch )
BWA_INDEX( ref_ch )
BWA_ALIGN( BWA_INDEX.out.bwa_index.combine(reads_ch) )
SAMTOOLS_SORT( BWA_ALIGN.out.aligned_bam )
SAMTOOLS_INDEX( SAMTOOLS_SORT.out.sorted_bam )
BCFTOOLS_MPILEUP( BWA_INDEX.out.bwa_index.combine(SAMTOOLS_INDEX.out.aligned_sorted_bam) )
BCFTOOLS_CALL( BCFTOOLS_MPILEUP.out.raw_bcf )
VCFUTILS( BCFTOOLS_CALL.out.variants_vcf )
}
workflow.onComplete {
println ( workflow.success ? """
Pipeline execution summary
---------------------------
Completed at: ${workflow.complete}
Duration : ${workflow.duration}
Success : ${workflow.success}
workDir : ${workflow.workDir}
exit status : ${workflow.exitStatus}
""" : """
Failed: ${workflow.errorReport}
exit status : ${workflow.exitStatus}
"""
)
}
/*
========================================================================================
THE END
========================================================================================
*/
- Make sure your
nextflow.configmatches below to be able to submit to the cluster
/*
========================================================================================
Custom Config File
========================================================================================
Default config options for HPC compute environments
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
//Profile config names for nf-core/configs
params {
config_profile_description = ''
config_profile_contact = ''
config_profile_url = ''
// Input parameters
genome = "${launchDir}/data/ref_genome/ecoli_rel606.fasta"
reads = "${launchDir}/data/trimmed_fastq/*_{1,2}.trim.fastq.gz"
// Output options
outdir = "results"
}
/*
========================================================================================
Nextflow Metrics & Reports
========================================================================================
*/
timeline {
enabled = true
file = "${params.outdir}/timeline.html"
}
report {
enabled = true
file = "${params.outdir}/report.html"
}
trace {
enabled = true
fields = 'task_id,name,status,exit,realtime,%cpu,%mem,rss,vmem,peak_rss,peak_vmem,rchar,wchar'
file = "${params.outdir}/trace.txt"
}
/*
========================================================================================
Base Executor config
========================================================================================
*/
executor {
queueSize = 2
}
/*
========================================================================================
Profiles - slurm,singularity,conda,docker
========================================================================================
*/
profiles {
sge {
process {
executor = 'slurm'
queue = 'my.q'
}
executor {
queueSize = 100
pollInterval = '15 sec'
}
}
conda {
process.conda = "${launchDir}/environment.yml"
}
singularity {
singularity.enabled = true
}
docker {
docker.enabled = true
}
}
Specific workflow entry points
By default, the unnamed workflow is assumed to be the main entry point for the script. Using named workflows, the entry point can be customised by using the -entry option of the run command. This allows users to run a specific sub-workflow or a section of their entire workflow script.
For example:
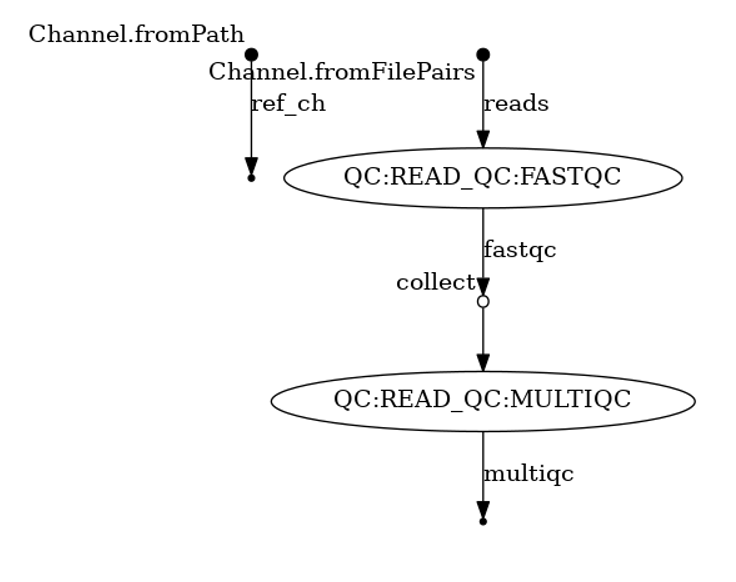
nextflow run variant-calling.nf -profile docker -entry QC -with-dag read_qc_dag.png
Output
executor > slurm (6) [a5/272a18] process > QC:READ_QC:FASTQC ([SRR2584866_1.trim.fastq.gz, SRR2584866_2.tri... [100%] 3 of 3 ✔ [af/1182f5] process > QC:READ_QC:MULTIQC ([SRR2584866_1.trim_fastqc.html, SRR2584866_1... [100%] 3 of 3 ✔ Pipeline execution summary --------------------------- Completed at: 2022-01-25T21:08:58.189-05:00 Duration : 1m 47s Success : true workDir : nextflow_tutorial/work
tree results/results/ ├── read_qc │ ├── multiqc_report.html │ ├── SRR2584863_1.trim_fastqc.html │ ├── SRR2584863_1.trim_fastqc.zip │ ├── SRR2584863_2.trim_fastqc.html │ ├── SRR2584863_2.trim_fastqc.zip │ ├── SRR2584866_1.trim_fastqc.html │ ├── SRR2584866_1.trim_fastqc.zip │ ├── SRR2584866_2.trim_fastqc.html │ ├── SRR2584866_2.trim_fastqc.zip │ ├── SRR2589044_1.trim_fastqc.html │ ├── SRR2589044_1.trim_fastqc.zip │ ├── SRR2589044_2.trim_fastqc.html │ └── SRR2589044_2.trim_fastqc.zip ├── report.html ├── timeline.html └── trace.txt 1 directory, 16 files
Quick Recap
- Nextflow DSL2 provides the capability to define reusable sub-workflow libraries, which enhances code modularity and reuse.
- Sub-workflows enable the encapsulation of a chain of processes that can be imported from other scripts and invoked as custom functions within a new workflow scope. This promotes reuse and manageability of workflow components.
- When running a Nextflow script, the
-entryoption of thenextflow runcommand can be used to specify the name of the workflow to be executed. This is especially useful when a script contains multiple workflow definitions.